This guide we’ll dive into whether coffee contains arginine, the potential benefits it offers, and any concerns you should consider.
This amino acid plays a role in various bodily functions, and understanding its presence in coffee could change how you view your daily brew.
The Presence Of Arginine In Coffee: A Deep Dive
Understanding the presence of this amino acid in coffee reveals both benefits and concerns. Arginine plays a role in various bodily functions, but its levels in coffee are not significant.
Is Arginine Naturally Present In Coffee Beans?
Yes, but in trace amounts. Coffee beans contain various amino acids, including L-arginine. However, arginine is a minor component in coffee. It’s not a primary amino acid compared to others, like glutamic acid or aspartic acid. The level of arginine in coffee can vary by bean. Factors affecting this include:
- Type of coffee varietal
- Processing methods
- Roasting techniques
Here is a brief overview of the typical amino acid content in coffee beans:
| Amino Acid | Average Content (per 100g of coffee beans) |
|---|---|
| L-Arginine | 0.1 – 0.2g |
| L-Glutamic Acid | 1.0 – 1.5g |
| L-Aspartic Acid | 0.8 – 1.2g |
The levels can differ based on the coffee varietal and its processing and roasting. Overall, the contribution of arginine to your diet from coffee remains low.
How Roasting Affects Arginine Content
Amino acids can be altered or reduced during the roasting process. High temperatures may cause some arginine to break down. This degradation can lead to lower amounts of arginine in the final brew.
Different roasting levels also impact arginine content:
- Light Roast: Retains more amino acids, including arginine.
- Medium Roast: Moderate retention of amino acids.
- Dark Roast: Generally has the lowest levels of amino acids.
Despite these changes, the overall impact on dietary arginine remains minimal. For most people, coffee is not a significant source of this amino acid.
Potential Benefits Of Arginine: Why It Matters
Arginine plays a crucial role in various body functions. Knowing its benefits can help you make informed choices about your diet.
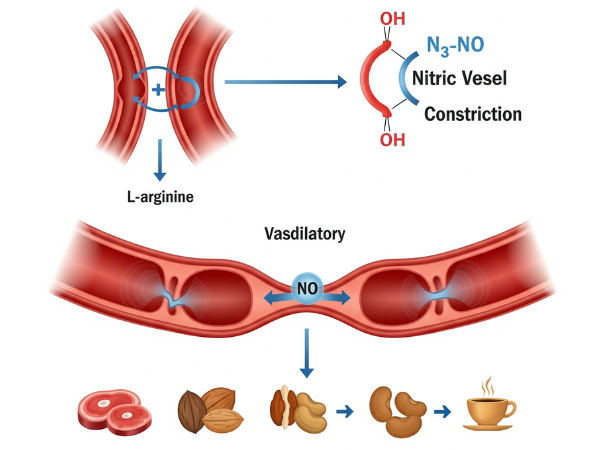
Arginine’s Role In The Body
Arginine, also known as L-arginine, is an amino acid. It is important for many processes in the body. Here are some key roles of arginine:
- Nitric Oxide Production: L-arginine is a precursor to nitric oxide (NO). NO is vital for many bodily functions.
- Vascular Health: NO helps relax blood vessels. This action can potentially aid blood flow.
- Immune Function: Arginine supports various aspects of the immune system. It helps the body defend against infections.
Arginine is also involved in protein synthesis. It assists in healing wounds and regulating hormone release. The body can produce arginine, but dietary sources are important for adequate levels.
Here is a simple table showing some benefits of arginine:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Blood Flow | Supports better circulation through blood vessel relaxation. |
| Enhanced Immune Response | Boosts the immune system’s ability to fight off illnesses. |
| Muscle Recovery | Aids in faster recovery after intense physical activity. |
How Dietary Arginine Is Typically Sourced
Dietary arginine comes from various protein-rich foods. Here are some primary sources:
- Meats: Poultry and fish are excellent sources.
- Dairy Products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt provide arginine.
- Nuts and Legumes: Almonds, walnuts, and beans are rich in arginine.
Some people take arginine supplements. Athletes often use them for improved performance. Those with specific health conditions may also benefit from supplements.
Coffee, while enjoyed by many, is not a significant source of arginine. Its contribution to daily arginine intake is negligible. Thus, relying on coffee for arginine is not advisable.
Are There Concerns About Arginine In Coffee?
While arginine is an amino acid that offers various benefits, many wonder if the small amounts found in coffee lead to any concerns. Are there risks associated with arginine in coffee? Let’s explore this topic further.
For Healthy Individuals: No Known Concerns
For most healthy individuals, there are no known concerns regarding arginine in coffee. The amount of arginine present is extremely low. Studies show that coffee has less arginine compared to many foods. The amount in coffee is far too small to cause effects.
- Coffee is not a significant source of arginine.
- Arginine levels in coffee are negligible.
- No adverse reactions reported in the general population.
People often drink coffee without worrying about arginine intake. Here’s a quick comparison of arginine levels in common foods versus coffee:
| Food Item | Arginine Content (per 100g) |
|---|---|
| Pumpkin Seeds | 4.7g |
| Peanuts | 3.0g |
| Chocolate | 1.0g |
| Coffee | 0.02g |
Coffee cannot be relied upon for arginine benefits. Healthy individuals can enjoy their coffee without concern. It is unlikely to trigger arginine-related issues in most people.
Specific Considerations For Sensitive Individuals
Some individuals may have specific concerns about arginine in coffee. For instance, people prone to herpes simplex virus outbreaks often avoid high arginine intake.
- Very rare sensitivities may react to trace compounds in coffee.
- Consult a doctor if you have specific dietary concerns.
It is essential for sensitive individuals to be aware of their dietary choices. While the arginine levels in coffee are extremely low, monitoring intake from other sources is wise.
Beyond Arginine: Other Key Compounds In Coffee
Understanding these components helps us appreciate coffee’s role in our diets. Let’s explore the key compounds found in coffee beyond arginine.

Beneficial Amino Acids And Compounds
Coffee contains a wide array of amino acids and compounds, though most are in small amounts. These beneficial substances contribute to coffee’s overall health-promoting properties.
- Other Amino Acids: Besides arginine, coffee has small amounts of other amino acids.
- Antioxidants: Coffee is packed with antioxidants that protect cells from damage.
- Polyphenols: These compounds help reduce inflammation and improve heart health.
- Chlorogenic Acids: Rich in chlorogenic acids, coffee offers significant health benefits.
These compounds work together to enhance the overall health benefits of coffee. Drinking coffee in moderation can support your well-being.
Caffeine: The Dominant Bioactive Compound
Caffeine is the primary stimulant in coffee. It is responsible for coffee’s alertness and energy effects. Most research on coffee’s effects revolves around caffeine.
Caffeine affects the central nervous system. It can improve focus, enhance mood, and increase energy levels. The following points highlight the metabolic impact of caffeine:
- Boosts metabolism and helps burn fat.
- Improves physical performance during exercise.
- Enhances cognitive function and concentration.
Studies show that caffeine can lead to short-term improvements in reaction time and mental alertness. The table below illustrates the average caffeine content in common coffee types:
| Coffee Type | Caffeine Content (mg per 8 oz) |
|---|---|
| Regular Brewed Coffee | 95 |
| Espresso | 63 |
| Decaffeinated Coffee | 5 |
Caffeine’s effects can vary by individual. Factors like tolerance and sensitivity play a role. Understanding caffeine’s impact can help you enjoy coffee while maximizing its benefits.
